Table Of Content
But there might also be a video for students to watch or an online class forum for discussion. There might even be a board game that students play to understand the history of the war. The primary focus is on finding ways to teach the material to the many types of learners in a classroom. UDLA is pleased to offer these no-cost professional learning opportunities.
How are the Guidelines related to the UDL framework?
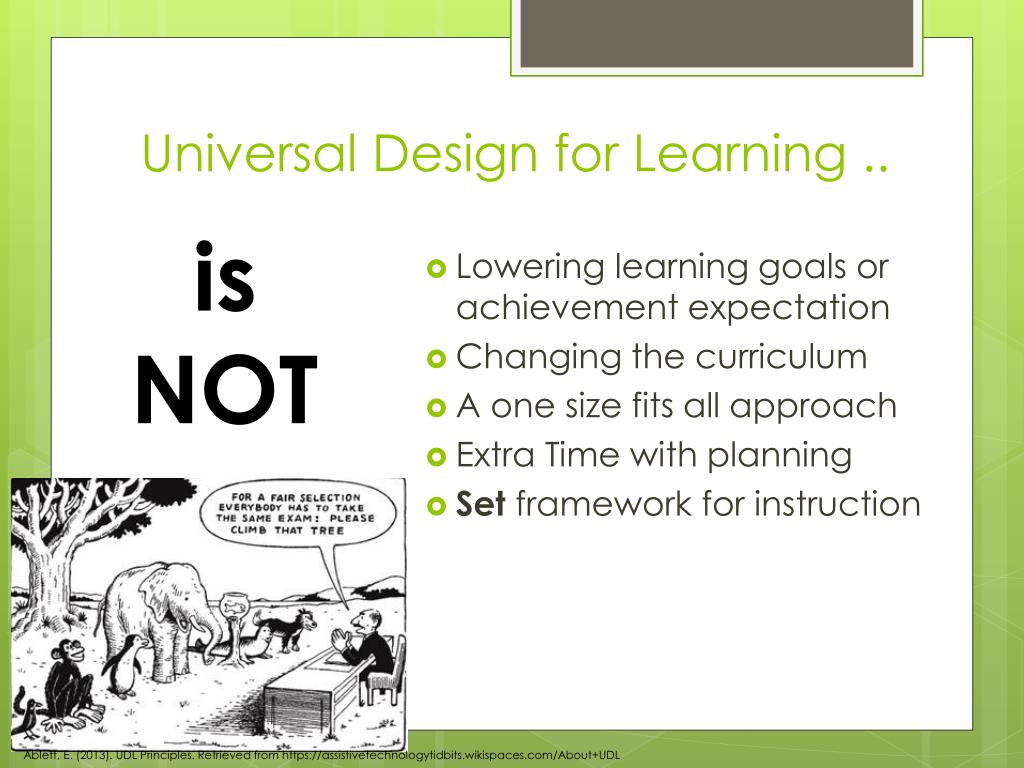
UDLA has options that support self-directed learners (resources, automated course) to more those that prefer more structure and guidance (in-person workshops, moderated online course work). Training and practice helps you slowly implement over time so that you aren’t overwhelmed but can slowly build towards mastery. As you improve in your implementation, your instruction and design will be more effective. UDL isn’t specifically for kids with learning and thinking differences. But it attempts to build in flexibility that can be adjusted for every student’s strengths and needs.
Supporting Students with Language Skills
Relay Resources Announces the Appointment of Dr. Lakshmi Balasubramanian to the Board of Directors - Newswire
Relay Resources Announces the Appointment of Dr. Lakshmi Balasubramanian to the Board of Directors.
Posted: Tue, 31 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
This means providing students with different ways to access and understand the content. For example, you might give a visual representation of the content, an audio version, and a written transcript. When teachers use UDL principles in their instruction, students learn more and achieve better outcomes. UDL provides ways to meet the needs of all learners, including those who are traditionally marginalized or left behind. The third core principle of UDL is to provide multiple means of engagement.
Universal Design for Learning: What Educators Need to Know
Inclusive school culture features training for special education and general education teachers, with the outcome of collaboration and shared responsibility. Fourth, there is research on specific applications of UDL within learning environments, including conditions necessary for implementation, common barriers, and lessons from the field. This new area of research is in its early stages but will take a more prominent place as full-scale curricular applications and system-wide implementations are developed. It should be noted that this is another area in which we greatly encourage contributions from the research field.
Actions
It’s about building in flexibility that can be adjusted for every student’s strengths and needs. You may, for example, have a student in your class with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Ways to reduce barriers could include helping them set a routine, learning more about their needs from their family, or referring them to a school specialist. When teaching, I aimed to address many barriers before we began a unit. Sometimes students didn’t have background knowledge, so we’d cover relevant topics and skills at the start. Other times, content wasn’t academically interesting or culturally relevant, so we found ways to tie it to their lives.
Action and expression
CAST created the Universal Design for Learning framework, and it remains one of our core levers of change to help make learning inclusive and transformative for everyone. UDL is regarded so highly that it’s mentioned by name in the nation’s main education law. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) encourages states and districts to use federal funding to help teachers expand the use of UDL.
UDL can be a powerful antiracism tool. Here's how. - District Administration
UDL can be a powerful antiracism tool. Here's how..
Posted: Tue, 09 Aug 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
It’s important to teach to each student’s individual strengths, skills and needs. This is true for all kids — not just kids with learning and attention issues. The evolution of CAST’s UDL Guidelines has been and continues to be a dynamic, collaborative, and developmental process. Since that time, we have collected and specifically solicited feedback from the field.
How can families support this at home?
Teachers can use UDL to design instruction that provides special education students with what they need and at the same time benefits all learners. UDL capitalizes on the concept that what is good for some is good for all. To support students with language skills, UDL champions the creation of learning environments that consider everyone. It extends beyond merely addressing disabilities, visible or otherwise, and speaks to the very essence of individual learning needs.

The third principle, multiple means of engagement, is about tapping into students' interests and motivations to foster deeper participation in the learning process. UDL emphasizes the significance of choice and relevance in learning tasks. This shift toward proactive, adaptable learning experiences is a significant departure from the traditional, rigid education model and is crucial in the pursuit of genuinely adaptive learning experiences for every student.
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework to improve and optimize teaching and learning for all people based on scientific insights into how humans learn. It also gives you some questions to consider and lists some examples of the principles in action. You can print a one-page version of this chart to have on hand while planning a lesson, activity, or routine for your students.
For example, you might allow students to use other forms of communication, such as speaking, writing, and drawing. Once you have assessed your students’ needs, you can customize your instruction to meet their individual needs. This could mean providing different representations of the content, different ways for students to interact with it, and different ways to express themselves. UDL is a research-based framework that places great emphasis on building self-directed learners. Learners will explore the factors that drive motivation and how those can be leveraged in the classroom.